Stack (กอง) เป็นโครงสร้างข้อมูลมีลักษณะการให้ข้อมูลเข้าออกคล้ายกับการวางของลงในกล่อง ของที่วางไว้ทีหลังจะอยู่บนสุด และจะถูกดึงออกมาก่อน ถ้าเป็นข้อมูลก็จะถูกดึงข้อมูลหลังสุดมาก่อน ถ้าเป็นการทำงานก็จะทำงานหลังสุดไล่ลงไปถึงงานแรกสุด มีชื่อเรียกกระบวนการนี้ว่า LIFO(Last in, First Out) เข้าทีหลังออกก่อน
Operations ของ stack ที่สำคัญได้แก่
- การนำข้อมูลเข้า (PUSH) เป็นการนำข้อมูลเข้าโดยข้อมูลที่เข้าทีหลังจะอยู่บนสุด (TOP)
- การนำข้อมูลออก (POP) เป็นการนำข้อมูลที่อยู่บนสุดออกโดยข้อมูลที่ถูก Pop จะถูกลบออกจาก stack
ตัวอย่างการทำงานของ Operation Push และ Pop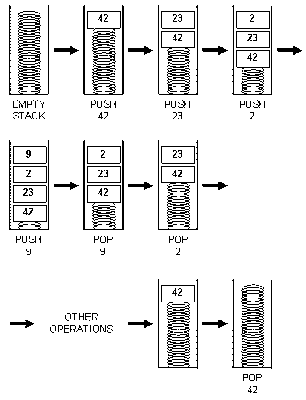 Implementation Stack การ implement Stack ทำได้ 2 วิธี คือ
Implementation Stack การ implement Stack ทำได้ 2 วิธี คือ
1. Array Implementation
2. Linked List Implementation
Stack Array Implementation
------------------------------------------------------------ กำลังทำการปรับปรุง------------------------------------------------------
Stack Linklist Implementation
- Stack Head ประกอบด้วย attributes 2 ตัวคือ 1. top (เป็น pointer ที่ชี้ไปยัง(เก็บ address) node ที่อยู่บนสุด) และ 2. count (เอาไว้นับจำนวน data ใน stack)
- Stack Node ประกอบด้วย attributes 2 ตัวคือ 1. data (ตัวแปรที่ใช้เก็บข้อมูลที่เรา Push) และ 2. link (เป็น pointer ที่ชี้ไปยัง second node)
เพื่อให้เห็นภาพเรามาสร้าง Stack Node โดยใช้ struct ของภาษา C กัน
/* Stack Node */
typedef struct
{
void* dataPtr; /* ใช้เก็บข้อมูล ที่ประกาศให้เป็น void เนื่องจากเราไม่รู้ว่าข้อมูลที่จะรับเข้ามานั้นเป็นข้อมูลชนิดไหน */
STRUCT node* link;
} STACK_NODE;
หลังจากสร้าง Stack Node แล้ว เรามาสร้าง Stack Head กัน
/* Stack Head */
typedef struct
{
int count;
STACK_NODE* top;
} STACK;
ต่อมาเรามาดู Stack's operations algorithm ที่เป็น pseudocode กัน
Create Stack
operation นี้ใช้สร้าง Stack Head โดย return address ของ stack head ซึ่งเวลาเรียกเราจะเรียกแบบนี้
STACK* stack;
stack = (STACK*) malloc(sizeof(STACK));
Algorithm createStack()
Creates and initializes metadata( stack head) structure
Pre : Nothing
Post: Structure created and initialized
Return: Stack Head
1. Allowcate memory for stack head
2. Set count to 0
3. Set top to null
4. return stack head
end createStack
Implement createStack with C
//========= createStack ============
STACK* createStack ()
{
STACK* stack;
stack = (STACK*) malloc(sizeof(STACK)); //Step 1.
stack->count = 0; //Step 2.
stack->top = NULL; //Step 3.
return stack; //Step 4.
}//end createStack
Push Stack
ตัวดำเนินการ pushStack หรือ insert เป็นการนำข้อมูลเข้าใน stack โดยมีจะต้องตรวจสอบด้วยว่ามีที่ว่าง(หน่วยความจำ) พอที่จะ push หรือไม่ algorithm เขียนได้ดังนี้
Algorithm pushStack (stack, data)
Insert (push) one item into stack.
Pre: stack passed by reference, data contain data to be push into stack
Post: data have been pushed in stack
Return: true if success, false if overflow
1. allowcate new node
2. store data in new node
3. make current top node the second node
4. make new node the top node
5. increment stack count
end pushStack
Implement pushStack with C
//========== pushStack ==============
bool pushStack (STACK* stack, void* dataInPtr)
{
STACK_NODE* newNodePtr;
newNodePtr = (STACK_NODE*) malloc(sizeof(STACK_NODE)); //Step 1.
if(!newNodePtr) // If memory full return false
{
return false;
} // end if
newNodePtr->dataPtr = dataInPtr; //Step 2.
newNodePtr->link = stack->top; // Step 3.
stack->top = newNodePtr; // Step 4.
(stack->count)++; // Step 5.
return true;
} // end pushStack
Pop Stack
ตัวดำเนินการ popStack เป็นการนำข้อมูลที่อยู่บนสุดออก แล้วทำการลบข้อมูลที่ pop ออกจาก Stack
Algorithm popStack(stack)
This algorithm pop the item on the top of the stack and return it to user.
Pre: stack passed by reference
Post: return pointer data to user if successful, return null if underflow
1.if (stack empty)
____1.1 set dataOut to null
2.else
____2.1 set dataOut to data in top node
____2.2 make second node the top node
____2.3 decrement stack count
3. end if
4. return dataOut
end popStack
Implement popStack with C
//=========== popStack ============
void* popStack (STACK*)
{
STACK_NODE* temp;
void* dataOut;
if(stack->count == 0) // Step 1.
{
dataOut = NULL; //Step 1.1
}
else // Step 2.
{
temp = stack->top;
dataOut = stack->top->dataPtr; // Step 2.1
stack->top = stack->top->link; // Step 2.2
free(temp);
(stack->count) --; // Step 2.3
} // end if
return dataOut;
}// end popStack
เสร็จแล้วนะครับสำหรับการ สร้าง Stack โดยการใช้ Link List
Full List of stackADT.h
// stackADT.h
// Stack ADT Definitions
//Stack Node
typedef struct
{
void* dataPtr;
STRUCT node* link;
} STACK_NODE;
//end stack Node
//Stack Head
typedef struct
{
int count;
STACK_NODE* top;
} STACK;
//end stack Head
/*========= createStack =================
This algorithm creates an empty stack.
Pre: Nothing
Post: Returns pointer to a null stack
-or- NULL if overflow
*/
STACK* createStack ()
{
STACK* stack;
stack = (STACK*) malloc(sizeof (STACK));
stack->count = 0;
stack->top = NULL;
return stack;
}//end createStack
/*============= pushStack =================
This function push an item to the stack.
Pre: stack is a pointer to the stack
dataPtr pointer to data to be inserted
Post: Data inserted into stack
Return: true if successful
false if overflow
*/
bool pushStack (STACK* stack, void* dataInPtr)
{
STACK_NODE* newNodePtr;
newNodePtr = (STACK_NODE*) malloc(sizeof(STACK_NODE));
if(!newNodePtr) // If memory full return false
{
return false;
} // end if
newNodePtr->dataPtr = dataInPtr;
newNodePtr->link = stack->top;
stack->top = newNodePtr;
(stack->count)++;
return true;
} // end pushStack
/*=============== popStack ===============
This function pops item on the top of stack
Pre: stack is pointer to a stack
Post: Return pointer data if successful
NULL if underflow
*/
void* popStack (STACK*)
{
STACK_NODE* temp;
void* dataOut;
if(stack->count == 0)
{
dataOut = NULL;
}
else
{
temp = stack->top;
dataOut = stack->top->dataPtr;
stack->top = stack->top->link;
free(temp);
(stack->count) --;
} // end if
return dataOut;
}// end popStack
